-
chevron_right
Premier League Wants GoDaddy to Identify Live Streaming Pirates
news.movim.eu / TorrentFreak · 4 days ago - 16:22 · 4 minutes
 England is widely regarded as the ‘home of football’ and the
Premier League
is its top competition, drawing hundreds of millions of viewers from all over the world.
England is widely regarded as the ‘home of football’ and the
Premier League
is its top competition, drawing hundreds of millions of viewers from all over the world.
Aside from the sportive stakes, the Premier League also has a vested interest in selling broadcast rights. These rights generate billions of pounds in revenue per year; a staggering amount unmatched by any other football league.
Broadcasters who secure these rights typically recoup their investment through the public, often in the form of subscriptions. However, not all football fans are willing to play this game and some seek out free or cheaper alternatives in the form of pirate streaming platforms.
In recent years, the Premier League has tried several legal avenues to tackle the piracy problem. In addition to obtaining blocking orders in multiple countries, the organization has been a driving force behind several lawsuits, some of which resulted in prison sentences .
Shutting down a pirate operation is always the preferred outcome for rightsholders, but it’s more easily said than done. Operators of streaming sites and services are typically aware of the risks and do their best to remain anonymous.
Premier League Takes Aim at GoDaddy Customers
In an attempt to lift this veil, the football organization went to a California federal court this week, hoping to discover the identities of operators connected to more than two dozen domain names.
The legal request isn’t targeted at the streaming sites directly. Instead, the Premier League requests a DMCA subpoena to compel domain registrar GoDaddy to hand over all information it holds on the operators. This doesn’t have to but might result in useful intel.
Domain names mentioned in the request (full list below) include live-kooora.com, 30.tv, live4.kooora-gooal.com, fctvlive.com, and soccertv4k.com. Some of these have a few hundred domain names, while others have several millions of monthly visits.

In addition, the Premier League requests information on several backend domains connected to the popular pirate streaming services EVPad and SVI Cloud. These two platforms are particularly popular in South East Asia and were previously called out as “notorious markets.”
EVPad, for example, was described as an “ extremely sophisticated ” pirate streaming service.
“A product purchased on behalf of the Premier League was found to provide access to over 1,700 channels, including 75 offering live sports broadcasts. The operators have been very careful to hide their location and identities, Premier League links them to Hong Kong and China.”

Identifying Pirates and More?
Through the requested DMCA subpoena, the Premier League hopes to gather more information on the people behind the sites and services.
Among other things, the football league asks GoDaddy for information that can identify people connected to the domains. This includes names, addresses, telephone numbers, and email addresses, payment information, and other account details.
Aside from the subpoena request, the Premier League sent a letter directly to GoDaddy, asking the domain registrar to remove or disable access to the infringing content. If not, it is expected that these sites will continue to broadcast similar pirate streams throughout the rest of the season.

At the time of writing, many of the domains and services listed in the application remain online. GoDaddy typically doesn’t take domains offline without a court order, so that doesn’t come as a surprise.
That said, if the DMCA subpoena is granted, GoDaddy will hand over the requested account holder information. These types of subpoenas only require a signature from a court clerk, so this will likely move forward.
Whether any of the information is usable to the Premier League is another question. Many pirate site owners use ‘inaccurate’ domain registration data and, since GoDaddy accepts cryptocurrency payments, the financial trail might run dead as well.
Update: The subpoena was signed by a court clerk.
—
The subpoena request and the associated paperwork, filed at a California federal court, is available here ( 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ).
A full list of all the domains mentioned can be found below. The request below includes several subdomains.
Websites
– live-kooora.com
– 5koora.live-kooora.com
– mpm24hd.com
– fctvlive.com
– koora-live.io
– yalla-shoot-as.com (redirects to yyallashoot.live)
– tarjetarojatvenvivo.net
– yalla–live.net
– kooora4lives.io (redirects to koora4live.ai)
– futbollibretv.me (redirects to futbollibretvhd.me)
– doomovie-hd.com (redirects to doomovie-hd.pro)
– streamlive7.com (redirects to match.fctvhd.com)
– live4.kooora-gooal.com
– 30.tv
– koooralive-tv.com (redirects to kooralive-tv.io)
– dooball2you.com
– dooballx.com
– soccertv4k.com
– futebolgratis.net
– baadooball.com
– dooballfree24hr.com
– herodooball.com
– kora-live-new.com
– kora-livee.com
– koora–live.com
– bein–match.com (redirects to tv.bein-match.pro)
SVI Cloud
– broker.6868a.cc
– 6868b.cc
– vpic.6868c.cc
– playback.f666666.xyz
EVPad
– appindex.google10sv.com
– v10js.google144.com
– sx.dl1717.com
– dlt.6868nbtc.com
– findpic.00005555.cc
– tm1.hdtvvip.com
– cdn_pic.0168861.com
From: TF , for the latest news on copyright battles, piracy and more.



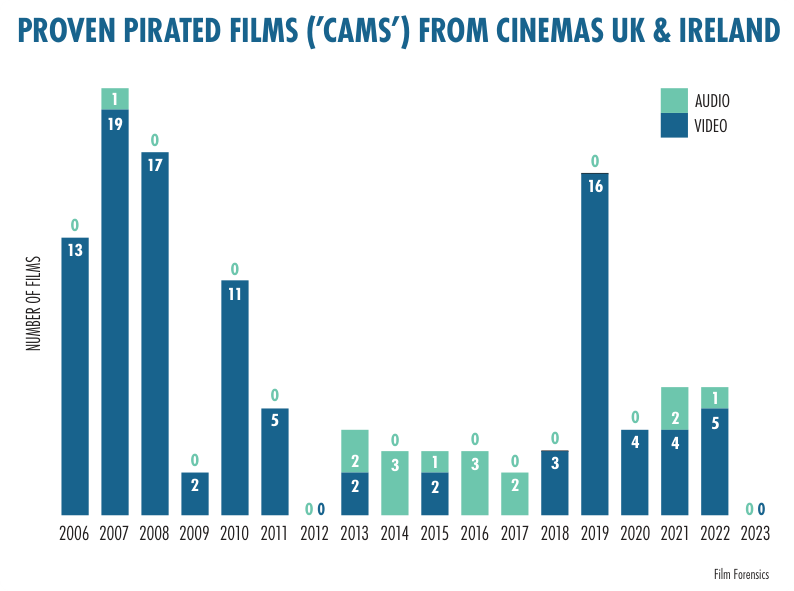
 Without doubt,
Without doubt,
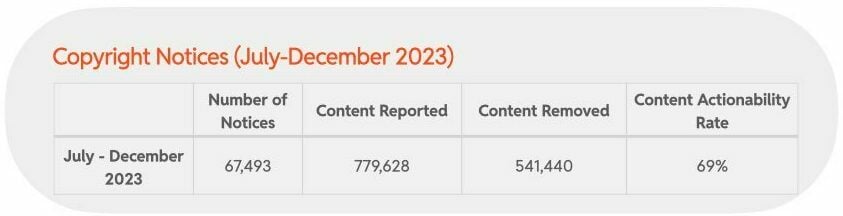
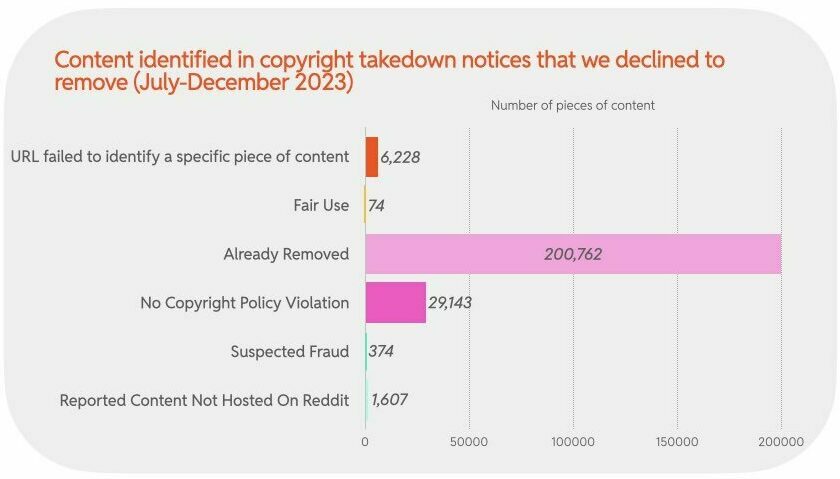




 For a long time, pirate site blocking was regarded as a topic most U.S. politicians would rather avoid.
For a long time, pirate site blocking was regarded as a topic most U.S. politicians would rather avoid.

