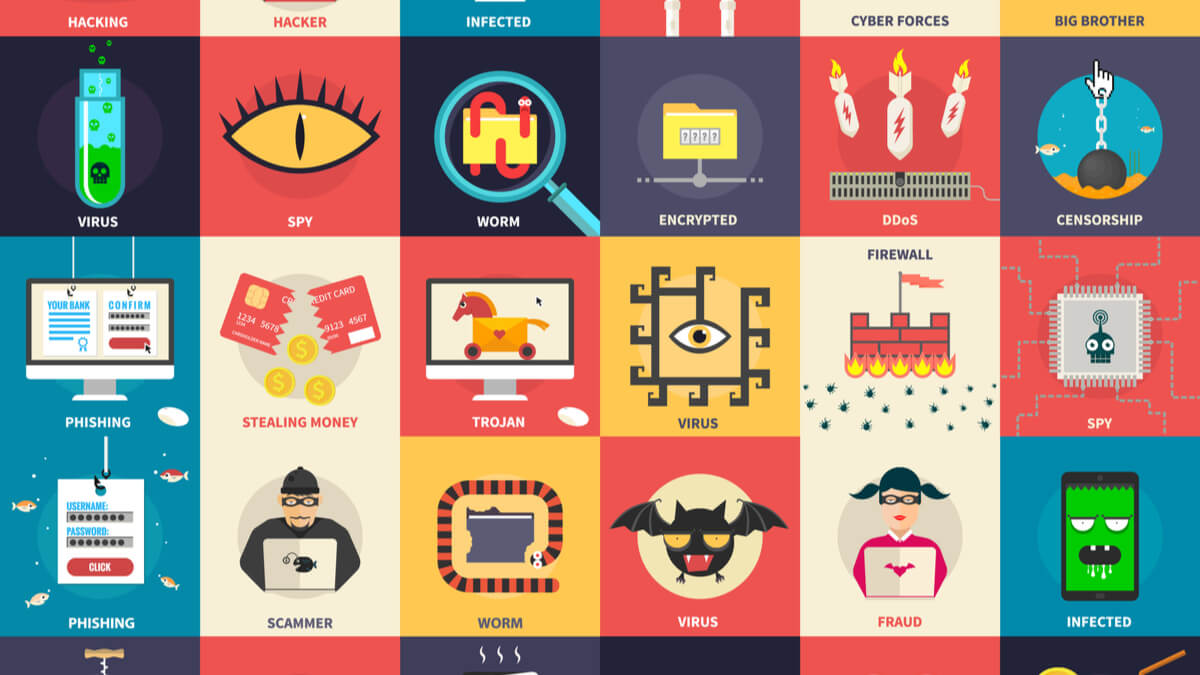
If you are among the people who consider malware, worms, and viruses to be the same thing, then you’re on the wrong track. Malware is an umbrella term for malicious software which includes all sorts of harmful elements like viruses, trojans, ransomware, bots, spyware, etc. So, let’s tell you about them in detail.
Have you ever tried to understand the difference between virus, trojan, worm, spyware, and malware? Even though they are meant to harm your device, steal your data, and spy on you, why are they named so differently? Basically, terms like viruses, trojans are all types of malicious software, or simply, malware.
Now, the first and foremost question arises, from where did the malware come? Who created the first virus?
Clearly, they are not some outer planet species, trying to harm us. In fact, the real truth is that they were not even created with an intention to harm someone.
The mention of malware goes back to 1949 when John von Neumann first developed the theoretical base for self-duplicating automation programs, but the technical implementation was not feasible at that time. The term “Computer Virus” was first used by
Professor Leonard M. Adleman
in 1981 in a conversation with Fred Cohen.
World’s first computer virus named ‘Brain’ was coded by two brothers, Basit Farooq Alvi and
Amjad Farooq Alvi
, who were from Lahore, Pakistan. Brain was meant to infect storage media based on MS-DOS FAT file systems. It was originally designed to infect the IBM PC; it replaced the boot sector of its floppy disk with the virus. The virus program changed the disk label to ©Brain and the defected boot sectors displayed this message:
Welcome to the Dungeon (c) 1986 Basit & Amjads (pvt) Ltd VIRUS_SHOE RECORD V9.0 Dedicated to the dynamic memories of millions of viruses who are no longer with us today – Thank GOODNESS!! BEWARE OF THE er..VIRUS: this program is catching program follows after these messages….$#@%$@!!
However, as you may presume, there was no evil intention behind this. Alvi brothers once justified Brain in their interview with TIME magazine; they created the virus only to protect their medical software from piracy. It was their countermeasure against copyright infringement acts.
Coming back to Malware, this is a malicious software designed to harm a computer that may or may not be connected to a network. Malware only gets into action when there is computer hardware involved in the game. Otherwise, the term Malware is of no use.
What are the types of Malware?
What is a Worm?
Worms are malware computer programs which have the ability to replicate themselves. Their sole objective is to increase their population and transfer themselves to another computer via the internet or through storage media. They operate like spies involved in a top-secret mission, hiding their movement from the user.
Worms don’t cause any harm to the computer; their replicating nature consumes hard drive space, thus, slowing down the machine. A couple of the infamous worms are SQL Blaster which slowed the internet for a small period and Code Red which took down almost 359,000 websites.
What is a Virus?
Viruses also have the ability to replicate themselves, but they do damage files on the computer they attack. Their main weakness lies in the fact that viruses can get into action only if they have the support of a host program. Otherwise, they’re just like a defeated warrior. They stick themselves to songs, videos, and executable files and travel all over the internet. W32.Sfc!mod, ABAP.Rivpas.A, Accept.3773 are some of the examples of virus programs.
The Virus Gang (Types of Computer Virus):
-
File Viruses
-
Macro Viruses
-
Master Boot Record Viruses
-
Boot sector Viruses
-
Multi-Partite Viruses
-
Polymorphic Viruses
-
Stealth Viruses
Feel free to Google any one of them if you like.
What is a Trojan?
Trojans are not like viruses or worms, and they are not meant to damage or delete files on your system. Their principal task is to provide to a backdoor gateway for malicious programs or malevolent users to enter your system and steal your valuable data without your knowledge and permission. JS.Debeski.Trojan is an example of Trojan.
Trojans derive their name from the ‘Trojan Horse’ tale in which the Greeks entered the city of Troy with the help of a wooden horse disguised as a gift. But the Trojan turned out to be a sweet poison, as depicted in the movie Troy.
The Trojan Gang (Types of Trojan):
-
Remote Access Trojans
-
Data Sending Trojans
-
Destructive Trojans
-
Proxy Trojans
-
FTP Trojans
-
Security Software Disabler Trojans
-
Denial-Of-Service Attack Trojans
Feel free to Google anyone of them if you like.
What is an Adware?
Adware are used to display advertisements on your computer’s desktop or inside individual programs. They generally come attached with free-to-use software. They are the primary source of revenue for the developers of those software programs.
Adware can’t be entirely described as Malware as they have no intention to harm your machine, they only track what advertisements you’re more interested in viewing and display the relevant ads on your computer screen. For some people, this can be alarming as it’s a breach of their privacy. Also, an attacker can stuff malicious code inside an adware program and use it to monitor users’ machine and even compromise it.
What is Rootkit?
Rootkits are a very dangerous category of malware as they are created with an aim to get remote access to a computer with full administrative privileges. Generally, a rootkit is a collection of different programs that work in a coordinated fashion to gain access and conceal its existence. They are also difficult to stop as they employ additional obfuscation mechanisms to hide their presence on the computer.
What is a Spyware?
Spyware programs also come attached with freeware. They track your browsing habits and other personal details and send it to a remote user. They can also facilitate installation of unwanted software from the internet. Unlike Adware, they work as a standalone program and do their operations silently.
What is a Spam?
You get very irritated when you receive unwanted emails from unknown senders; these are called Spams or junk emails. And the process of flooding the internet with the same message is called Spamming, done for the purpose of commercial advertising. These junk emails may sometimes contain Viruses or Trojans that enter your system as soon as you open the mail.
What is a Bot?
Bots or robots are automated processes that are designed to interact over the internet without the need of human interaction. They can be used for good and bad intentions. An evil-minded person can create a malicious Bot that is capable of infecting the host on its own. After transmitting itself to the host device, a Bot creates a connection with central servers which act as the command centers for the all infected hosts attached to that network called Botnet.
A bot’s skills include stealing passwords, logging keystrokes, analyzing network traffic, relay spam, launching DoS (Denial of Service) attacks, and opening backdoors on infected hosts.
Bots can be seen as the advanced form of Worms. Their infection rate and the tactic is more effective than that of Worms. These malicious Bots are created after a lot of hard work done by their malignant creators.
What is a Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malware that can alter the normal operation of your machine. It encrypts the data and prevents you from using your computer partially or wholly. Ransomware programs also display warning messages asking for money to get your device back to normal working condition.
What is a Keylogger?
As its name suggests, keylogger software is used to record the keystroke actions of a computer user. While it may be used for ethical purposes of measuring user behavior and engagement, the term is generally used for software that aims to record such actions without the knowledge of users. With a help of a keylogger, a notorious actor can know your email details, password, credit card details, messages you type, etc.
Why people create malware?
After reading all this, you might be thinking why people create malware. Here are some reasons which might compel a coder to write malware programs:
-
Take control of a person’s computer for personal or professional reasons.
-
To get financial benefits. This also includes hackers raising money for a cause. Last year, we heard about a ransomware attack where hackers were collecting money to feed people. But it doesn’t mean what they were doing was right.
-
To steal confidential data.
-
To prove their point. For instance, by performing a security breach on a vulnerable system.
-
To take down an individual computer or a complete network.
and the list goes on….
How can you protect your computer from malware?
-
Keep your system up to date.
-
Use genuine software.
-
Install an antivirus software and update it regularly.
-
Set-up a firewall, may it be custom as provided by antivirus software. Windows has an inbuilt firewall option in case you don’t want to use a custom firewall.
-
Never open unknown emails that generally reside in your Spam folder.
-
Never open unknown links, use online website safety checker tools if you’re not sure to open a website.
By taking these simple measures, you can effectively keep your machine free from Malware and other potential threats.
The post
What Is The Difference: Viruses, Worms, Ransomware, Trojans, Malware, Spyware, Rootkit
appeared first on
Fossbytes
.
 chevron_right
chevron_right