-
 chevron_right
chevron_right
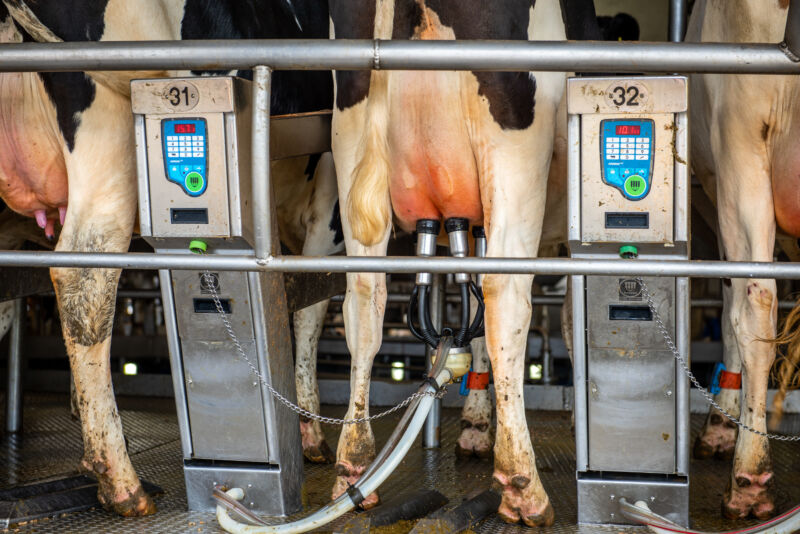
20% of grocery store milk has traces of bird flu, suggesting wider outbreak
news.movim.eu / ArsTechnica · Yesterday - 14:26 · 1 minute

Enlarge (credit: Getty | Jeffrey Greenberg )
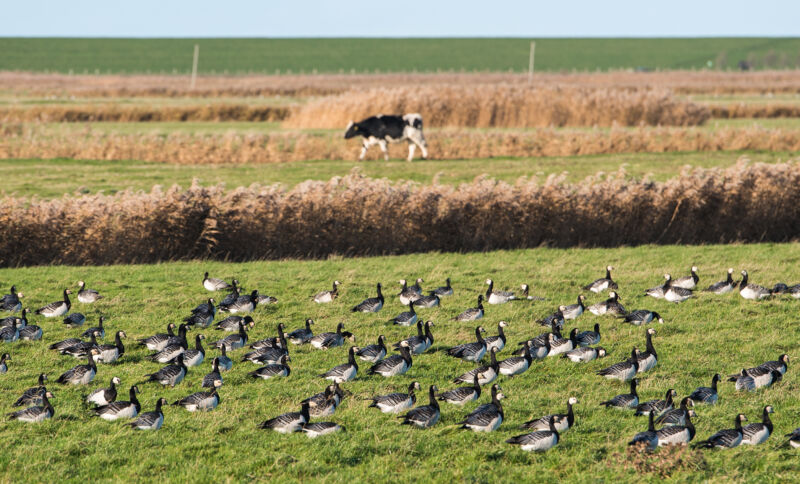
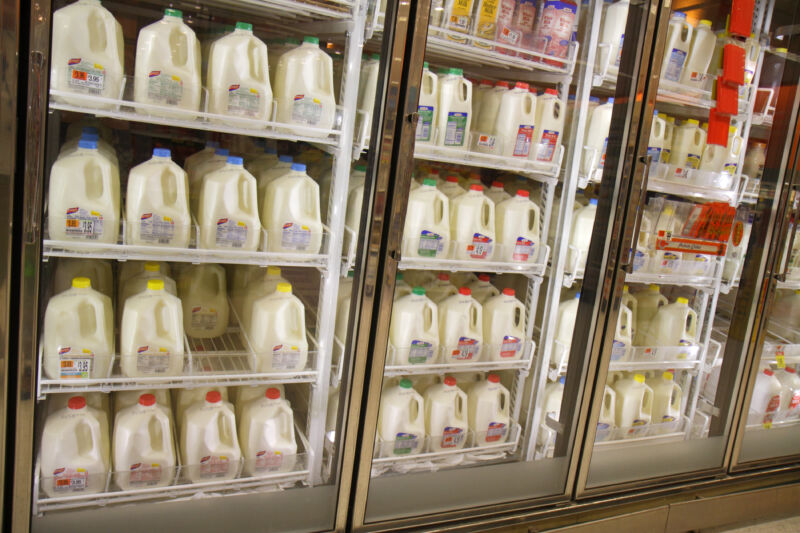
The Food and Drug Administration reported late Thursday that about 20 percent of retail milk samples from around the country tested positive for genetic fragments of the bird flu , aka highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) virus H5N1. While retail milk is still considered to be safe, the finding suggests that the spread of the virus in cows is more extensive than is currently known.
The FDA used a test called quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), which can only detect the presence of genetic fragments. In pasteurized retail milk, it is highly likely that those genetic snippets are merely remnants of virus particles destroyed during pasteurization. The FDA is currently conducting additional testing using egg inoculation tests, a gold-standard for detecting a live virus, to confirm the effectiveness of pasteurization. Meanwhile, the director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Jeanne Marrazzo, told reporters Wednesday that tests at the agency's federal labs so far did not identify live virus from any of its sampling. Additionally, several previous studies have found that pasteurization of eggs—which is done at a lower temperature than it is for milk—was effective at destroying H5N1.
While experts are largely unconcerned with the safety of commercial milk, the potential for wide, unrecognized spread of bird flu in dairy herds is alarming. To date, the US Department of Agriculture has only confirmed infections in 33 herds in eight states . The FDA acknowledged that of its positive samples, "a greater proportion of positive results [are] coming from milk in areas with infected herds." But with tens of thousands of dairy herds in the US, the finding suggests that infections are being missed. It does not necessarily suggest that 20 percent of all cows are affected, since milk is pooled for commercial distribution. But 33 herds alone are unlikely to explain the high prevalence.